1. 数据库连接池
1.1. 数据库连接池技术
- 为解决传统开发中的数据库连接问题,可以采用数据库连接池技术。
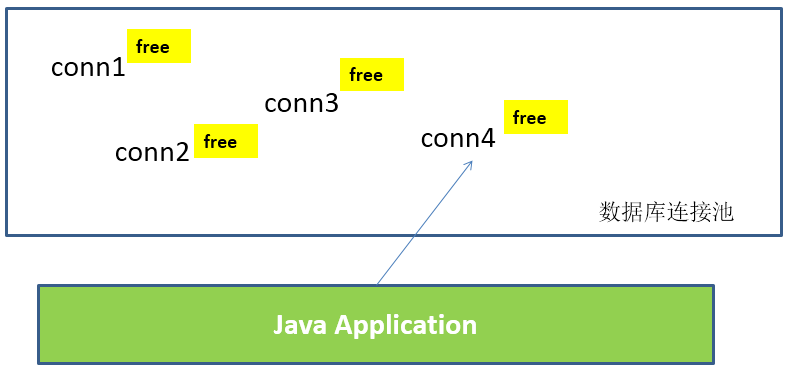
- 数据库连接池的基本思想:就是为数据库连接建立一个“缓冲池”。预先在缓冲池中放入一定数量的连接,当需要建立数据库连接时,只需从“缓冲池”中取出一个,使用完毕之后再放回去。
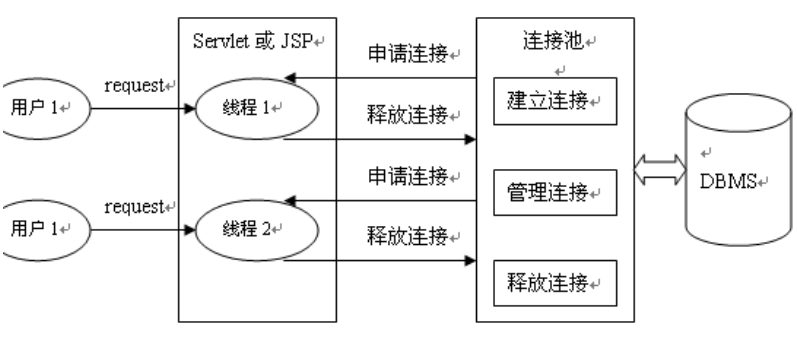
- 数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是重新建立一个。
- 数据库连接池在初始化时将创建一定数量的数据库连接放到连接池中,这些数据库连接的数量是由最小数据库连接数来设定的。无论这些数据库连接是否被使用,连接池都将一直保证至少拥有这么多的连接数量。连接池的最大数据库连接数量限定了这个连接池能占有的最大连接数,当应用程序向连接池请求的连接数超过最大连接数量时,这些请求将被加入到等待队列中。
工作原理:
1.2. 多种实现
JDBC 的数据库连接池使用 javax.sql.DataSource 来表示,DataSource 只是一个接口,该接口通常由服务器(Weblogic, WebSphere, Tomcat)提供实现,也有一些开源组织提供实现:
-
DBCP 是Apache提供的数据库连接池。tomcat 服务器自带dbcp数据库连接池。速度相对c3p0较快,但因自身存在BUG,Hibernate3已不再提供支持。
-
C3P0 是一个开源组织提供的一个数据库连接池,**速度相对较慢,稳定性还可以。**hibernate官方推荐使用
-
Proxool 是sourceforge下的一个开源项目数据库连接池,有监控连接池状态的功能,稳定性较c3p0差一点
-
BoneCP 是一个开源组织提供的数据库连接池,速度快
-
Druid 是阿里提供的数据库连接池,据说是集DBCP 、C3P0 、Proxool 优点于一身的数据库连接池,但是速度不确定是否有BoneCP快。
DataSource 通常被称为数据源,它包含连接池和连接池管理两个部分,习惯上也经常把 DataSource 称为连接池
DataSource用来取代DriverManager来获取Connection,获取速度快,同时可以大幅度提高数据库访问速度。 -
特别注意:
- 数据源和数据库连接不同,数据源无需创建多个,它是产生数据库连接的工厂,因此整个应用只需要一个数据源即可。
- 当数据库访问结束后,程序还是像以前一样关闭数据库连接:conn.close(); 但conn.close()并没有关闭数据库的物理连接,它仅仅把数据库连接释放,归还给了数据库连接池。
1.3. 以Druid为例
public class TestDruid {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream ("druid.properties");
Properties prop = new Properties ();
assert inputStream != null;
prop.load (inputStream);
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource (prop);
//从连接池中获取连接
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection ();
System.out.println (conn);
}
}
配置文件druid.properties
# 2. 数据库连接url
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc1?rewriteBatchedStatements=true&useSSL=false&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
# 3. 用户名
username=root
# 4. 密码
password=jia1895247349
# 5. 驱动名称
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 6. 初始化的连接个数
initialSize=10
# 7. 最大连接个数
maxActive=20
# 8. 最大空闲个数
maxWait=1000
# 9. 属性类型是字符串,通过别名的方式配置扩展插件,常用的插件有: 监控统计用的filter:stat日志用的filter:log4j
# 10. 防御sql注入的filter:wall
filters=wall
2. DBUtils
2.1. DbUtils
提供如关闭连接、装载JDBC驱动程序等常规工作的工具类,里面的所有方法都是静态的。
主要方法如下:
-
public static void close(…) throws java.sql.SQLException:
DbUtils类提供了三个重载的关闭方法。这些方法检查所提供的参数是不是NULL,如果不是的话,它们就关闭Connection、Statement和ResultSet。
-
public static void closeQuietly(…):
这一类方法不仅能在Connection、Statement和ResultSet为NULL情况下避免关闭,还能隐藏一些在程序中抛出的SQLEeception。
- public static void commitAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException:
用来提交连接的事务,然后关闭连接.
-
public static void commitAndCloseQuietly(Connection conn):
用来提交连接,然后关闭连接,并且在关闭连接时不抛出SQL异常。
-
public static void rollback(Connection conn)throws SQLException:
允许conn为null,因为方法内部做了判断
-
public static void rollbackAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException
-
public tstaic void rollbackAndCloseQuietly(Connection)
-
public static boolean loadDriver(java.lang.String driverClassName):
这一方装载并注册JDBC驱动程序,如果成功就返回true。使用该方法,你不需要捕捉这个异常ClassNotFoundException。
2.2. QueryRunner类
该类简单化了SQL查询,它与ResultSetHandler组合在一起使用可以完成大部分的数据库操作,能够大大减少编码量。
- QueryRunner类提供了两个构造器:
- 默认的构造器
需要一个 javax.sql.DataSource 来作参数的构造器
- 默认的构造器
- QueryRunner类的主要方法:
- 更新
public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException:
用来执行一个更新(插入、更新或删除)操作。
- 插入
public T insert(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler rsh, Object... params) throws SQLException:
只支持INSERT语句,其中 rsh - The handler used to create the result object from the ResultSet of auto-generated keys. 返回值: An object generated by the handler.即自动生成的键值.
- 批处理
public int[] batch(Connection conn,String sql,Object[][] params)throws SQLException:
INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE语句
public T insertBatch(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler rsh,Object[][] params)throws SQLException:
只支持INSERT语句
- 查询
public Object query(Connection conn, String sql, ResultSetHandler rsh,Object... params) throws SQLException:
执行一个查询操作,在这个查询中,对象数组中的每个元素值被用来作为查询语句的置换参数。该方法会自行处理 PreparedStatement 和 ResultSet 的创建和关闭。
......
2.3. ResultSetHandler接口及实现类
该接口用于处理 java.sql.ResultSet,将数据按要求转换为另一种形式。
-
ResultSetHandler 接口提供了一个单独的方法:Object handle (java.sql.ResultSet .rs)。
-
接口的主要实现类:
ArrayHandler:把结果集中的第一行数据转成对象数组。
ArrayListHandler:把结果集中的每一行数据都转成一个数组,再存放到List中。
**BeanHandler:**将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中。
**BeanListHandler:**将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中,存放到List里。
ColumnListHandler:将结果集中某一列的数据存放到List中。
KeyedHandler(name):将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,再把这些map再存到一个map里,其key为指定的key。
**MapHandler:**将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个Map里,key是列名,value就是对应的值。
**MapListHandler:**将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,然后再存放到List
**ScalarHandler:**查询单个值对象
public class TestDBUtils {
private Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties ();
properties.load (Objects.requireNonNull (ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream ("druid.properties")));
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource (properties);
return dataSource.getConnection ();
}
@Test
public void insert() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner ();
String sql = "insert into student(name,email,age) values(?,?,?)";
int result = runner.update (getConnection (),sql,"ketelin","ketelin@kilric.com",20);
System.out.println ("插入了" + result + "条记录。");
}
@Test
public void delete() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner ();
String sql = "delete from student where id = ?";
int result = runner.update (getConnection (),sql,6);
System.out.println ("删除了" + result + "条记录");
}
@Test
public void queryInstance() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner ();
String sql = "select * from student where id = ?";
BeanHandler<Student> handler = new BeanHandler<> (Student.class);
Student student = runner.query (getConnection (),sql,handler,1 );
System.out.println (student);
}
//将结果的第一列保存在对象数组中
@Test
public void queryAsArray() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner ();
String sql = "select * from student where id < ?";
ArrayHandler handler = new ArrayHandler ();
Object[] res = runner.query (getConnection (),sql,handler,5);
for (int i = 0; i < res.length ; i++) {
System.out.println (res[i]);
}
}
//将结果的所有列保存在对象List中
@Test
public void queryForList() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner ();
String sql = "select * from student";
BeanListHandler<Student> handler = new BeanListHandler<> (Student.class);
List<Student> list = runner.query (getConnection (),sql,handler);
list.forEach (System.out::println);
}
}